Product Description
Introduction
ZD Leader has a wide range of micro motor production lines in the industry, including DC gear motor, AC gear motor,brushless DC motor,planetary gear motor, helical AC gear motor, hypoid gear motor, drum motor and planetary gearbox, etc. Through technical innovation and customization, we help you create outstanding application systems and provide flexible solutions for various industrial automation situations. We have a comprehensive global product development network, with pre-sales and after-sales centers in the United States, Germany, Japan, India, Vietnam and other countries.
Our Advantages
Range Of Gear Motor
Pleas click the click button to view more detailed specification for each serie of Gear Motor.
After Sales Service
Customized Product Service
Company Profile
FAQ
Q: What’re your main products?
A: We currently produce Brushed Dc Motors, Brushed Dc Gear Motors, Planetary Dc Gear Motors, Brushless Dc Motors, Stepper motors, Ac Motors and High Precision Planetary Gear Box etc. You can check the specifications for above motors on our website and you can email us to recommend needed motors per your specification too.
Q: How to select a suitable motor?
A:If you have motor pictures or drawings to show us, or you have detailed specs like voltage, speed, torque, motor size, working mode of the motor, needed lifetime and noise level etc, please do not hesitate to let us know, then we can recommend suitable motor per your request accordingly.
Q: Do you have a customized service for your standard motors?
A: Yes, we can customize per your request for the voltage, speed, torque and shaft size/shape. If you need additional wires/cables soldered on the terminal or need to add connectors, or capacitors or EMC we can make it too.
Q: Do you have an individual design service for motors?
A: Yes, we would like to design motors individually for our customers, but it may need some mold developing cost and design charge.
Q: What’s your lead time?
A: Generally speaking, our regular standard product will need 15-30days, a bit longer for customized products. But we are very flexible on the lead time, it will depend on the specific orders.
Please contact us if you have detailed requests, thank you !
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Operating Speed: | Constant Speed |
|---|---|
| Number of Stator: | Single-Phase |
| Species: | Y, Y2 Series Three-Phase |
| Rotor Structure: | Winding Type |
| Casing Protection: | Closed Type |
| Number of Poles: | 2 |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How do manufacturers ensure the quality and reliability of induction motors?
Manufacturers employ several measures and quality control processes to ensure the quality and reliability of induction motors. Here are some key steps taken by manufacturers:
- Design and Engineering:
- Manufacturers invest significant resources in the design and engineering of induction motors.
- Experienced engineers use advanced computer-aided design (CAD) software to develop motor designs that meet performance specifications and industry standards.
- Design considerations include efficient cooling, optimal winding configurations, and robust mechanical construction.
- Material Selection:
- Manufacturers carefully select high-quality materials that meet or exceed industry standards.
- They use premium-grade electrical steel laminations for the motor core to minimize energy losses and maximize efficiency.
- Copper or aluminum conductors with appropriate insulation are chosen for the motor windings to ensure reliable electrical performance.
- Stringent Manufacturing Processes:
- Manufacturers follow stringent manufacturing processes to ensure consistency and quality throughout production.
- They employ advanced machinery and automation to achieve precise manufacturing tolerances and reduce human error.
- Quality control checks are performed at various stages of the manufacturing process to identify and rectify any issues.
- Testing and Inspection:
- Induction motors undergo rigorous testing and inspection procedures to verify their performance and reliability.
- Manufacturers conduct various tests, such as electrical tests, mechanical tests, insulation tests, and performance tests.
- These tests ensure that the motors meet or exceed specified parameters for voltage, current, power factor, efficiency, torque, and speed.
- Inspection processes involve visual inspections, dimensional checks, and verification of critical components.
- Certifications and Compliance:
- Reputable manufacturers ensure that their induction motors comply with relevant industry standards and regulations.
- They obtain certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems, and adhere to specific standards like IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) or NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association).
- Certifications and compliance demonstrate the manufacturer’s commitment to producing high-quality and reliable products.
- Customer Feedback and Continuous Improvement:
- Manufacturers value customer feedback and use it as a valuable source of information for continuous improvement.
- They actively engage with customers to understand their needs and address any concerns or issues promptly.
- Feedback helps manufacturers refine their designs, manufacturing processes, and quality control measures to enhance the overall quality and reliability of their induction motors.
By implementing these measures, manufacturers strive to ensure that their induction motors meet the highest standards of quality and reliability. Continuous improvement and adherence to industry best practices enable manufacturers to deliver products that perform consistently and reliably in a wide range of applications.

How do induction motors handle challenges like variations in voltage and frequency?
Induction motors are designed to handle challenges such as variations in voltage and frequency, and they have mechanisms in place to ensure reliable operation under these conditions. Here’s a detailed explanation of how induction motors handle these challenges:
Voltage Variations:
Induction motors are typically designed to operate within a certain voltage range. However, they can handle variations in voltage to some extent. Here’s how they handle voltage variations:
- Stator Windings: The stator windings of an induction motor are designed to withstand voltage fluctuations. The insulation materials used in the windings provide protection against voltage surges and dips. The winding design and the number of turns are optimized to ensure the motor can operate within the specified voltage range while maintaining reliable performance.
- Voltage Regulation: Voltage regulators or voltage stabilizers can be used to control and regulate the voltage supplied to an induction motor. These devices ensure that the motor receives a stable voltage within the acceptable range, even in the presence of fluctuations in the power supply. Voltage regulation helps maintain consistent motor performance and prevents damage that could occur due to excessively high or low voltages.
- Motor Protection Devices: Induction motors are often equipped with protective devices such as overvoltage relays and undervoltage relays. These devices monitor the incoming voltage and trigger appropriate actions if the voltage exceeds or falls below the predefined thresholds. For example, if the voltage exceeds a certain limit, the overvoltage relay may trip and disconnect the motor from the power supply to prevent damage.
Frequency Variations:
Induction motors are designed to operate at a specific frequency, typically 50 or 60 Hz, depending on the region. However, they can handle certain variations in frequency while maintaining reasonably stable performance. Here’s how induction motors handle frequency variations:
- Synchronous Speed: The speed of an induction motor is determined by the frequency of the power supply and the number of poles in the motor. When the frequency varies, the synchronous speed of the motor changes accordingly. However, the motor’s actual operating speed, known as the slip speed, remains relatively constant. This allows the motor to maintain its output power and torque, although the speed may vary slightly.
- Motor Design: The design of induction motors takes into account the expected frequency variations in the power supply. The number of poles and the winding configuration are selected to ensure that the motor can operate within an acceptable range of frequencies while maintaining optimal performance. The motor’s mechanical and electrical characteristics are carefully matched to achieve the desired operating parameters under different frequency conditions.
- Frequency Converters: In some cases, frequency converters or Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) are used to control the speed of induction motors. These devices can vary the frequency supplied to the motor, allowing precise control of the motor speed. Frequency converters are particularly useful in applications where the motor needs to operate at different speeds or where the power supply frequency is not compatible with the motor’s design.
- Motor Protection Devices: Similar to voltage variations, induction motors can be equipped with protective devices to monitor the frequency of the power supply. These devices can detect significant deviations from the expected frequency and trigger appropriate actions, such as shutting down the motor or providing an alarm signal. Protecting the motor against extreme frequency variations helps prevent damage and ensures safe operation.
In conclusion, induction motors are designed to handle challenges such as variations in voltage and frequency. Through appropriate design considerations, voltage regulation mechanisms, protective devices, and the use of frequency converters, induction motors can operate reliably and maintain reasonably stable performance even in the presence of fluctuations in the power supply. These features contribute to the versatility and resilience of induction motors in various industrial applications.
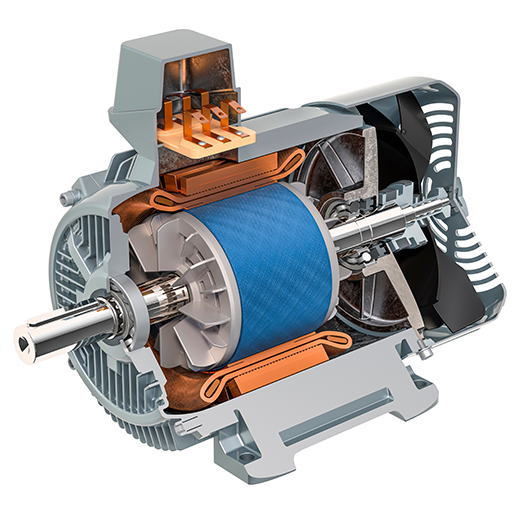
How do induction motors differ from other types of electric motors?
Induction motors differ from other types of electric motors in several ways. Here’s a detailed explanation of the key differences:
- Operating Principle:
- Induction motors operate based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a rotating magnetic field induced by the stator windings interacts with the rotor conductors to produce torque.
- In contrast, other types of electric motors, such as DC motors, synchronous motors, and stepper motors, operate on different principles and have distinct mechanisms for generating motion.
- Power Supply:
- Induction motors typically operate on AC (alternating current) power supply. The stator windings are connected to an AC power source, which produces a rotating magnetic field.
- On the other hand, DC motors require a DC power supply, and synchronous motors may operate on either AC or DC power supply, depending on their design.
- Speed Control:
- Induction motors have a fixed speed determined by the frequency of the AC power supply and the number of poles in the motor. The speed can be adjusted to some extent by changing the supply frequency or using variable frequency drives (VFDs).
- DC motors, on the other hand, offer precise speed control by adjusting the voltage applied to the motor armature.
- Synchronous motors can operate at a fixed speed determined by the frequency of the AC power supply, but they can also be controlled using specialized techniques such as field weakening or using electronic drives.
- Stepper motors operate in discrete steps, allowing precise control of position and speed.
- Construction:
- Induction motors are typically constructed with a squirrel cage rotor, which consists of short-circuited conductive bars or loops. The rotor construction makes them simple, robust, and suitable for high-speed applications.
- Other types of motors may have different rotor constructions, such as wound rotors in some AC motors or permanent magnets in brushless DC motors.
- Starting Mechanism:
- Induction motors are self-starting, meaning they can start without the need for additional starting mechanisms. The rotating magnetic field generated by the stator windings induces voltage and current in the rotor, enabling the motor to start rotating.
- Some other types of motors, such as DC motors, require external starting mechanisms like starting resistors or electronic controls to initiate rotation.
- Efficiency and Maintenance:
- Induction motors are known for their high efficiency and low maintenance requirements. They have a simple construction with no brushes or commutators, which reduces wear and eliminates the need for regular maintenance.
- Other types of motors, such as brushed DC motors, may require brush replacement and periodic maintenance.
These are some of the main differences between induction motors and other types of electric motors. Each type of motor has its advantages, disadvantages, and specific applications, depending on the requirements of the system or industry where they are used.


editor by CX 2024-03-28